- Sectors
- Aerospace & Defense
- Big science
- Biotechnology
- Fintech
- Work at ARQUIMEA
- Insights
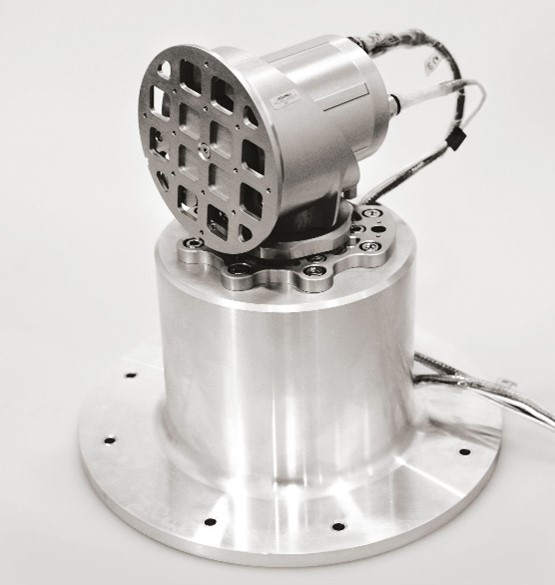

PRE2POS stands for PREcision-based drive mechanisms for high-PREcision energy efficient POSitioning devices. It is an R&D project implemented under the European Union’s Horizon2020 research and innovation programme and carried out by a Consortium formed by ARQUIMEA and the Italian company Phi Drive. PRE2POS was focused on validating novel rotary actuators using an innovative motor that takes advantage of the micrometric deformation displacement of piezoelectric stacks to achieve infinite rotary or linear motion. The project also involved the analysis and definition of the next steps towards the industrialization and commercialization of the resulting product.
The final goal is to include the rotary actuators in in key equipment and mechanisms used in spacecraft, such as solar array drive mechanisms, antenna pointing mechanisms or deployment mechanisms like booms and masts where high precision, low weight, energy efficiency and low manufacturing costs are constantly sought by the end users.
The project was successfully completed in 2020 with the formal approval of the European Commission.
Currently, the main commercial actions have already started and are oriented to small new satellite platforms still under development that might be keener on using this disruptive technology to become more competitive.
The project team needed to develop a new cutting-edge solution aiming to improve the technical and economic performance of the equivalent products currently available.
A complete rotary actuator was developed and validated for the space market considering the dimensioning of the drive motor and the optimization of its performances.
Moreover, a smart design was developed to guarantee a cost-effective integration of the Pre2pos motor components into ARQUIMEA customized gimbal design.
Finally, since the idea was to use this solution in future small sat platforms that require off-the-self short lead time products, the gimbal needed to be a standard product, cost affordable and with a short lead time.
ARQUIMEA’s gimbal powered by Phi Drive’s motor device is a two-axes positioner which function is to precisely direct a load. The gimbal is formed by two motors driven by piezoelectric stacks with electric redundancy. It includes two degrees of freedom: the rotation in roll and yaw axes.
The system design shows moderate torque capabilities (torque/mass ratio is +95% compared to existing solutions), providing system simplification with a very high accuracy and resolution and a very low backlash to the user avoiding the use of additional gearboxes.
ARQUIMEA gimbal is based on the coordinated actuation of the several piezoelectric stacks separated in two phases which operates with certain phase shift. This system provides individual rotative steps as small as 0.002°with a moderate speed.
Adapting the working parameters, the output torque or the rotational speed can be adjusted to the technical requirements needed. Also, the position control can be adapted to the different needs, as this gimbal controls the position by an optical encoder.
ARQUIMEA and Phi Drive implemented the entire solution for the release and deployment of antennas, scientific instruments and reflectors’ pointing and positioning.
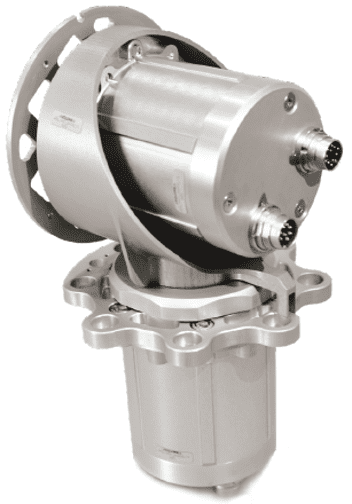
A total of three EQM models of the system were produced to validate the solution. The acceptance test campaign of the EQM models was performed and completed at the end of 2019. This solution was successfully tested considering the design and operation requirements and conditions for space applications.
ARQUIMEA’s gimbal together with Phi Drive’s motor proved to be the right solution for the target applications in small sats.